Explain the Different Fields of an Ip Packet Header
The minimum use of the IP header is 20 bytes consisting of five 32 bit words. Every packet on the Internet has an assigned protocol value and ICMP IPPROTO_ICMP or 1 UDP IPPROTO_UDP or 17 and TCP IPPROTO_TCP or 6 each own a code.
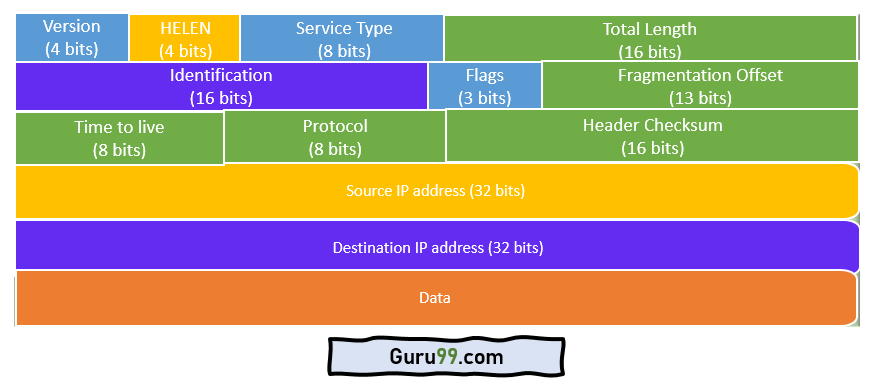
Ip Packet Header Format Fields
The preamble field is 7 bytes long.

. The values for the type of Upper Layer PDU are same as IPv4s. IPv6 packet may contain zero one or more extension headers but these should be present in their recommended order. The 13-bits field Fragment Offset is used in a similar way as IPv4.
The next 8 bits are then reserved. Ethernet header contains five fields. Destination Address 32-bit address of the Receiver or destination of the packet.
This field is used to indicate either the type of Extension Header or if the Extension Header is not present then it indicates the Upper Layer PDU. Lets understand each field in detail. Total length the length of the entire packet header data.
The value of the upper layer protocol field is ICMP 0X01 3. The second bit represents whether a packet is allowed to be fragmented Dont FragmentmdDF or split into multiple pieces. With Quality of service a network may choose how to handle the packets.
It is used to define the IP version. This document describes version 4. The Version field indicates the format of the internet header.
Version of the IP protocol 4 bits which is 4 for IPv4. It is used on packet-switched Link Layer networks such as Ethernet. IPV4 header format is of 20 to 60 bytes in length contains information essential to routing and delivery consist of 13 fields VER HLEN service type total length identification flags fragmentation offset time to live protocol header checksum source IP address Destination IP address and option padding where each has its own features and provides essential data.
The first bit is always set to 0. It does not include the data field and the value. The extension header mechanism is a very important part of the IPv6 architecture.
The minimum length is 20 bytes and the. Header Checksum This field is used to keep checksum value of entire header which is then used to check if the packet is received error-free. The field called Next Header 8 bits specifies the header type like an upper layer protocol header or IPv6 extension header.
The packet datagram header is as shown below. This is same as TTL in IPv4. This header contains fourteen fields.
The Flags field is used to control how a specific IP packet is treated by a device. For IPv4 this field has a value of 4. The type of service is an 8 bits header field each bit has a meaning for quality of service.
Precedence The first three bits are for precedence. Within the IP packet header what is the value in the upper layer protocol field. The minimum value for this field is 5 and the maximum is 15.
Each byte alternatively stores 1 and 0 to make the pattern 10101010. Preamble SFD Destination Source and Type. The first 3 bits are the priority bits.
IPv4 Datagram Header Size of the header is 20 to 60 bytes. Precedence means the priority of an IP packet in case. Source Address 32-bit address of the Sender or source of the packet.
Internet Header Length is the length of the internet header in 32 bit words and thus points to the beginning of the data. Preamble bytes help the receiving device to identify the beginning of an Ethernet frame. The field is 3 bits and is formatted as follows.
Options This is optional field which is used if the value of IHL is greater than 5. The next 8 bits are then reserved. 143 rows You have learned Internet Protocol Version 4 IPv4 Internet Protocol Version 4 IPv4 Datagram Header different fields in an IPv4 header and IPv4 Datagram fragmentation.
The sequence number is a 32 bit field that indicates how much data is sent during the TCP session. The protocol tells the system how to treat the incoming packet. IPv4 uses the best effort delivery method which does not provide a guarantee of delivery.
IPv4 Internet Protocol version 4 is the fourth version of the Internet Protocol IP. This field is used to stop packet to loop in the network infinitely. The next Header field of IPv6 fixed header points to the first Extension Header and this first extension header points to the second extension header and so on.
How many bytes are in the payload of the IP datagram. IP header length 4 bits which is the number of 32 bit words in the header. Lets walk through all these fields.
The minumum value is 20 bytes and the maximum value is 60 bytes. This is a 16 bit field that specifies the port number of the receiver. Priority and Type of Service specifies how the datagram should be handled.
How many bytes are in the IP header. Explain how you determined the number of payload bytes. It is used to define the length of the header.
IPv4 packet is made up of a header and a data section. The type of service in the Ip header is for controlling the quality of service of Internet Protocol packet traffic. Low Delay High Throughput Reliability 8 bits.
When you establish a new TCP connection 3 way handshake then the. This is a 16 bit field that specifies the port number of the sender. Alternatively you can set it directly if you elect direct IP header manipulation IP_HDRINCL.
B Header length 4 bit. Source Address the IP address of the original sender of the packet Destination Address the IP address of the final destination of the packet Options not normally used but when used the IP header length will be greater than five 32-bit words to. Header length the length of the header in 32-bit words.
It contains a string of 7 bytes. The different fields of an IPv4 header are Version IHL Type of Service Total Length Flags Fragment offset TTL Time to Live Protocol Header Checksum Source IPv4 Address Destination IPv4. A Version 4 bit.
Note that the minimum value for a correct header is 5. The value 4 defines the packet as IPv4 while value 6 defines the packet as IPv6.

No comments for "Explain the Different Fields of an Ip Packet Header"
Post a Comment